- Home Page
- Ham Radio Links
- Sat Tv Dx Links
- Digital Modes
- My Archives
- My Other Hobbies
- Linux Ham Links
- Where I Live
|
DMR TYT Dmr Software is HERE BEST PRACTICE As this is a global network, users need to realise the
impact of each talk group on users around the globe as well as nationally and
within a region. Time slot 1 is the most busiest with other countries also
having other talk groups on this slot so opening a lot of repeaters prevents
other network users globally from using the time slot. Ideally the choice of
talk group should be as to open the least repeaters possible. As much as some
say, activity breeds activity or that the talk group is quiet, note that users
may be using another talk group on the same slot that you do not have access
to. Itís not to limit people from using the facilities on the network but more
of having consideration for our fellow amateurs using the network. Also itís worth bearing in mind that not all users have
display radios or maybe scanning the talkgroups, so itís a good idea to mention
which TG youíre on as part of your call-in or handover transmission. TG1, TG2 & TG13 TG1 opens all repeaters globally, TG2 opens all repeaters in
Europe and TG13 opens all repeaters in English speaking countries Ė several
hundred repeaters can be affected by one of these talk groups. Thus these talk
groups are ďcalling channelsĒ meant to establish a contact and qsoís should be
kept limited to a few minutes. Try to prevent UK only qsoís on these talk
groups by moving to UK Wide user activated talk groups TG80 & TG81 or a
more local talk group depending on where the users are located. Other user
activated talk groups (TG113, TG119, TG123 & TG129) can also be used to
reduce the number of repeaters being opened. TG235 This has a similar impact as TG1, TG2 & TG13 Ė it opens
all repeaters within the UK. It prevents other UK users from utilising any
other slot 1 talk group. Where possible, users should use the user activated
talk groups TG80 & TG81 which are UK only or TG113, TG119, TG123 &
TG129 which are World Wide TG8xx REGIONAL
Other Digital Modes The digital modes provide a wonderful opportunity for those of us who would like to work on the HF bands but find CW too difficult and SSB phone prohibitive because of interference problems. These modes require very little power to work the world. Generally 25 to 50 watts is plenty of power. The digital modes are comparable to CW in that their bandwidths are very narrow. Bandwidths generally range from about 30 to 200 Hz compared with SSB which is 2,100 Hz. This is a huge difference and one of the main reasons why the digital modes are so effective at low power. Because of their low power and modulation schemes, the digital modes do not interfere with telephones and answering machines in the neighborhood the way the SSB often does.
The digital modes are easy to set up and get operating. What is needed is an HF rig, a computer running one of the many software programs that are available either for free (most are) or for a small purchase price, and a hardware interface between the computer and radio. Most computers come with a sound card and these modes work via the sound card input and output circuits. A fairly easy interface between the sound card and radio can be built for around £3.00 or a very nice and very adequate interface can be purchased that will handle any chore you might throw at these modes. Best of all, the digital modes are incredible easy to use. The major software programs utilize a waterfall display that shows all of the signals currently operating on the band. All you have to do is click on a signal with your mouse, and the QSO pops up on your computer screen. It doesnít get any easier than that. The digital modes described in this article are mainly found on the High Frequency bands and will require a General class license or above (except on 10 meters where a Technician with morse code privileges can operate from 28.100 to 28.300 MHz). There is a wide choice of digital modes to choose from. However, the most popular modes today are PSK31, BAUDOT (RTTY), MFSK-16, and PACTOR. PSK31 is the most popular of the digital modes because it is very effective at low power, is easy to set up (it requires only an HF radio and a computer with a sound card), and its waterfall display makes it extremely easy to use. Baudot RTTY is the second most popular, particularly for DX and contest work. RTTY is the oldest of the digital modes. However, new software with waterfall displays and using the computerís sound card as the HF radio interface has given the old standby a new look. MFSK-16 is one of the newest modes that shows considerable promise. It is a good weak signal performer, reportedly better than PSK31, particularly for DX contacts that involve signal paths that pass through the Earthís polar regions. It is a little more difficult to operate than PSK31 but does use a waterfall display and sound card radio interface. PACTOR is the most popular of the error correcting class of digital modes that includes AMTOR, Clover, and G-TOR. These modes utilize relatively complex protocols that automatically detect and recover from transmission errors through a combination of forward error correction and automatic retransmissions. They are excellent for message handling in that they deliver error free text to the computer screen. However, they are more than what is needed for most casual amateur radio QSOs. Because of their complex protocols, these modes require a multi-mode hardware controller box between the computer and HF radio. The multi-mode controller makes these modes more expensive to implement and a little more difficult to operate than the modes using waterfall displays and sound card interfaces. One point to mention about the sound card interface is that once you have it installed, you can switch between the various modes that use the interface (PSK31, RTTY, MFSK-16, and others) by simply activating the appropriate software package on your computer. Where on the HF bands do you find hams using the digital modes? The following chart shows you were to look. |
Digital CQ freqs
|
BAND |
PSK31 |
RTTY |
MFSK-16 |
PACTOR |
|
80 Meters |
3.580 - 3.584 |
3.580 - 3.620 |
3.610 |
3.580 - 3.620 |
|
40 Meters |
7.070 - 7.074 |
7.080 - 7.100 |
7.080 |
7.080 - 7.100 |
|
30 Meters |
10.130 - 10.140 |
10.130 - 10.140 |
10.130 - 10.140 |
10.130 - 10.140 |
|
20 Meters |
14.070 - 14.074 |
14.070 - 14.095 |
14.080 |
14.070 - 14.095 |
|
18 Meters |
18.100 - 18.105 |
18.100 - 18.105 |
18.100 - 18.105 |
18.100 - 18.105 |
|
15 Meters |
21.070 - 21.074 |
21.070 - 21.100 |
21.080 |
21.070 - 21.100 |
|
12 Meters |
24.920 - 24.925 |
24.920 - 24.925 |
24.920 - 24.925 |
24.920 - 24.925 |
|
10 Meters |
28.120 - 28.124 |
28.070 Ė 28.120 |
28.130 |
28.070 - 28120 |
from an artical By Eddie Pierce, WB6DFW
Digital Modes Software
PSK***RTTY
|
SOFTWARE |
MODE |
STATUS |
LAST UPDATE |
|
PSK31/63-radiocontrol |
FREE |
Ver.3.9.2.1 and 2.0 |
|
|
PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver.2.117 |
|
|
PSK31/63 |
FREE |
Ver. 2.13 |
|
|
PSK31/63 |
FREE |
Beta 4.0f |
|
|
PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver. 2.1b |
|
|
PSK31/63,/RX/Pactor |
FREE |
Ver. 2.0 |
|
|
PSK31(RX-20 ch.) |
DEMO |
Ver. 5.0 |
|
|
PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver. 2.23 |
|
|
PSK31/63,RTTY,TNC |
FREE |
Ver. 4.5.0 |
|
|
PSK31 |
FREE |
------ |
|
|
CW-DOMINOEX-THROB(X)-OLIVIA(+64/2000) -MT63-MFSK-RTTY-QPSK/BPSK31/63/125-SSTV |
FREE |
||
|
RX only. PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver. 2.1 |
|
|
SMARTPSK-DXPSK |
PSK31(RX25 ch.) |
FREE |
Ver. 2.6a/1.6 |
|
PSK31,TNC |
73$ |
Ver. 3.21 |
|
|
PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver. 1.08 |
|
|
RTTY |
FREE |
Ver. 1.65D |
|
|
PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver. 0.9.1 |
|
|
PSK31,Packet,TNC |
79.95$ |
Ver. 3.0 |
|
|
RTTY, PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver. 4.03 |
|
|
PSK31/63 |
FREE |
Ver 2.5 |
|
|
RTTY-PSK-MFSK-SSTV |
---- |
Ver 3.3 |
|
|
PSK31/63 |
24.95$ |
Ver.1.0 |
|
|
PSK |
FREE/Shareware |
Ver. 7.0/4.5 |
*** MFSK *** HELL *** THROB *** MT63 *** PACKET *** CW *** OLIVIA*** WinDRM *** ALE ***
|
SOFTWARE |
MODE |
STATUS |
LAST UPDATE |
|
CW . SDR, IQ |
75$ |
Ver. 1.0 |
|
|
OLIVIA-AID |
FREE |
||
|
THROB |
FREE |
Ver. 2.6 |
|
|
CW,TX via SC+PTT |
49.9$ |
Ver. 4.061 |
|
|
Packet |
49$ |
14/05/2007 |
|
|
Packet |
FREE |
----- |
|
|
HELL,MT63,MFSK |
FREE |
2004 |
|
|
CW |
35$ |
Ver. 1.50 |
|
|
FSK441/B/C,JT44, JT65,JT6M,JT2,JT4 |
FREE |
||
|
WSJT Home PageMAP65+LinRAD |
JT65 |
FREE |
Ver.0.8 |
|
DominoEX |
FREE |
19 Dec. 2005 |
|
|
CW |
FREE |
------ |
|
|
CHIP 64/128 |
FREE |
Ver. 1.3 01/26/07 |
|
|
Digital voice |
FREE |
6 JAN 08 |
|
|
ALE mod 141A |
FREE |
Ver.0.498/0.529 |
*** SSTV *** DIGSSTV *** DSP ***
Some Tv Pictures Recieved in 2009-2010
|
SOFTWARE |
MODE |
STATUS |
LAST UPDATE |
|
HAM-WINDRM |
FREE |
||
|
DIGSSTV |
FREE |
12/26/08 |
|
|
DIGSSTV,WinDRM |
FREE |
Ver.3.11 |
|
|
DIGSSTV/SSTV |
FREE |
09/12/2004 |
|
|
DIGSSTV |
FREE |
Ver. 1.8d |
|
|
SSTV |
120$ |
Ver. 1.6.17 |
|
|
SSTV |
FREE |
Ver. 1.11G |
|
|
SSTV,RTTY,FAX |
60 EUR |
Ver. 1.40pre |
|
|
DSP |
FREE |
Ver. 1.11 |
|
|
DSP |
FREE |
12/03/2004 |
|
|
DSP-Mixer |
39.95$ |
21/02/06 ver 1.9.1 |
|
|
DSP filter |
FREE |
Ver.2.5.2.1 |
LOGBOOKS ( supports digital modes)
|
SOFTWARE |
MODE |
LAST UPDATE |
|
|
TNC, RTTY,PSK31/63,TNC |
45 EUR |
Ver. 3.16/Ver. 3.3 |
|
|
RTTY,PSK,TNC |
89.95$ |
Ver. 7.02 |
|
|
RTTY, PSK,TNC, MMVARI |
FREE |
Ver. 3.9 |
|
|
WriteLog(contest) |
RTTY,PSK31,TNC |
75$ |
Ver.10.65 |
|
N1MM(contest) |
PSK31,RTTY,TNC |
FREE |
Ver.6.x.x |
|
PSK31,RTTY |
50$ |
Ver. 4.48 |
|
|
PSK31,TNC |
99$ |
Ver. 1.0 |
|
|
75$ |
Ver. 1.8h9 |
||
|
CwGet+TrueTTY |
49$ |
Ver. 2.47 |
|
|
CwGet+DigiPan+MixW+TrueTTY |
35$ |
Ver.1.30 |
|
|
MixW+Hamscope+TrueTTY |
65$ |
Ver. 5.2 |
|
|
Hamscope+Digipan+MixW |
129$ |
Ver. 8.0 |
|
|
PSK31/63 |
FREE |
Ver. 2.1.180 |
|
|
MixW |
FREE |
Ver. 3.2.01 |
|
|
RTTY |
59$ |
Ver. 9.4.3 |
|
|
PSK31/63 |
89.54$ |
Ver.5.0 |
|
|
MMTTY Spectrum analysis and audio recorder |
FREE |
Ver. 6.2 |
|
|
RTTY-MMTTY |
35 EUR |
Ver. 3.7 |
MULTIMODE
|
SOFTWARE |
MODE |
STATUS |
LAST UPDATE |
|
RX only .RTTY, CW, PSK31 |
FREE |
||
|
PSK-MFSK-RTTY |
FREE |
1.2.0 |
|
|
MT63,MFSK,PACTOR I(TX/RX), SSTV, DIGSSTV,ACARS,THROB,APRS,CCW/CW,PSKFEC31/ PSK31/63/PSKAM,PSK220F,RTTY,HELL,CW,FSK, OLIVIA,PAX/PAX2,Chip64/128,Video ID, Domino EX FEC, DIGIVOICE,RTTYM,CONTESTIA,TCP/IP digital modem, ALE400(ALE141A)-JT65 |
FREE! |
Ver.4.7 |
|
|
CW-OLIVIA(+64/2000)-DOMINOEX-MT63-THROB(X)-MFSK-RTTY-QPSK/BPSK31/63/125, SSTV |
FREE! |
||
|
RTTY (Baudot code), ASCII (7 or 8 bits), PSK31 (BPSK and QPSK), BPSK63, AMTOR-FEC (SITOR-B, NAVTEX), MultiFSK-16, MultiFSK-8. HF-PACKET and UHF-PACKET (AX25) are supported in KISS-TNC emulation mode. SELFEC SITOR, AMTOR-ARQ (SITOR-A) and DTMF |
35$ |
Ver.2.60 |
|
|
CW,Packet,RTTY,MFSK,PSK31 |
FREE |
Ver. 1.56 |
|
|
RTTY,PSK31/63,CW,MFSK,MT63,OLIVIA,THROB,Hell,Packet,Pactor, SSTV+RTTY-M-CONTESTIA |
50$ |
19 Feb.07 |
|
|
DSP, Spectrum,RTTY, SSTV, PSK,CW,HELL+many other modes |
99 EUR |
Ver. X.12 |
|
|
DSP, Spectrum,RTTY, SSTV,PSK+many other modes |
232 EUR. |
Ver. 5.2 |
|
|
RTTY(FSK,AFSK), MFSK, BPSK31,GMSK |
FREE |
Ver. 0.42 |
LF resources(135.7 -137.8 kHz)
|
Software |
Mode |
STATUS |
UPDATE |
|
PSK31,RTTY, QRSS/DFCW |
DEMO |
Ver. 2.71 b4 |
|
|
QRSS/DFCW |
45$ |
Ver. 11.0 |
|
|
QRSS/DFCW |
FREE |
Ver.1(134) |
|
|
QRSS/WSJT |
FREE |
V. 2.13 |
Agw Packet Software
|
Software |
Mode |
Status |
Update |
|
APRS |
FREE Tnx author , SK |
Ver. 2.03 |
|
|
Packet |
FREE Tnx author , SK |
Ver. 6.80 |
|
|
SAT-APRS |
FREE |
Ver. 4.1.1 |
|
|
Packet |
FREE |
Ver.2.06 |
|
|
APRS |
49$ |
21.12.2006 |
Windows Sound Card Software
Digital modes groups on YAHOO
|
|
CI-V SOFTWARE
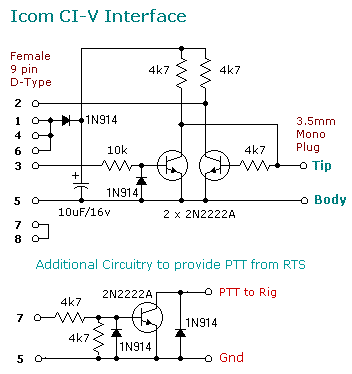
Ci-v interfaceIcom and Yaesu appears to delight in charging outrageous prices for all transceiver accessories, so many Hams improvise instead. A few circuits have been published for CI-V interfaces, Here is a very simple CI-V interface, originally described by OK2WY. Although the circuit doesn't conform exactly to the RS-232 specification, it does work well and has the advantage of being easily constructed inside a 9 pin D-type shell. Please note that the resistor value 4K7 means 4700 ohms. The transistor types are not critical, I just happen to have plenty of 2N2222As. I've used this interface on various PC's and also Notebooks with both an FT857d and to Program a FT7800. No problems have been experienced even at . It has also worked successfully when using a USB/Serial adapter from a notebook. If a PTT function is required from the COM port, pin 7 (RTS) can be used to provide this facility. The circuit is powered by DTR (pin4). I experienced some problems with YPLog using this power source. If YPLog is configured to use PTT from either the Parallel port or a different serial port from the one used by the CI-V Interface, the program drops the DTR signal, resulting in no power to the interface. This is easily resolved by powering the circuit from RTS (pin 7) instead of DTR (pin4). I have also used this interface to program my Yaesu VX5R. Only a change of connector to a 4 pole minijack plug was required. Probably the interface can be used with other HTs, although I have not tried it.
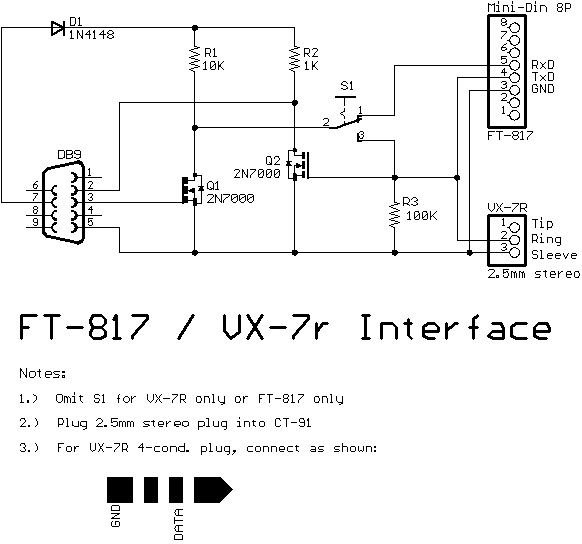
Yaesu Programming InterfaceThere are two 2N7000 MOSFET transistors, one diode and three resistors. You can eliminate the DPDT switch if you only need to use it with one rig.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A interface for the ft847 is HERE |